The fabled lost Ark of the Covenant -- described in the Bible as the sacred container of the Ten Commandments -- lies buried near the top of Mt. Tsurugi on the Japanese island of Shikoku, according to local legend.

The Ark, which was built according to instructions given by God to Moses in a prophetic vision on Mt. Sinai, is sacred to Jews and Christians alike and is said to possess great supernatural powers.
Many people also know it from the 1981 action film "Indiana Jones and the Raiders of the Lost Ark," which follows the adventures of archeologist Indiana Jones as he thwarts Nazi efforts to obtain the Ark and harness its powers for evil.

Scene from "Raiders of the Lost Ark"
But what really happened to the Ark? According to the biblical book of Kings, King Solomon -- a King of Israel -- built a large temple in Jerusalem to house the sacred object, and it was kept there during his reign (970-930 BC) and beyond. Centuries later, in 586 BC, the Babylonians conquered Jerusalem and destroyed the temple. Some historians suggest the Ark was probably carted off by the Babylonians or perhaps destroyed in battle, but nobody knows for sure. Its fate remains one of the world's great unsolved mysteries.
Since its disappearance, various groups around the world claim to have discovered or obtained possession of the Ark. The list of locations includes Jordan, Egypt, Ethiopia, southern Africa, France, UK, Ireland -- and Japan.

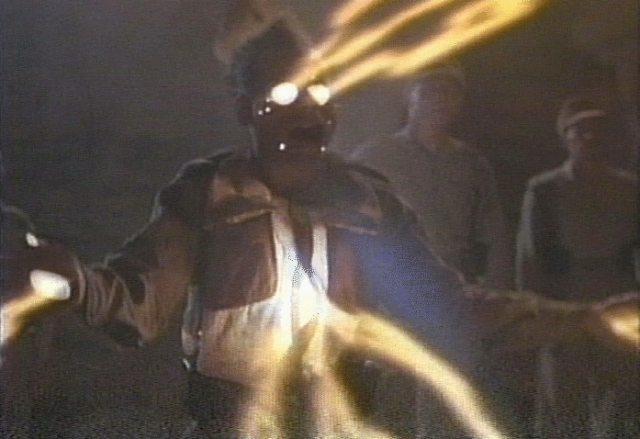
Did a lost tribe of Israel carry the fabled Ark to Mt. Tsurugi?
In Japan, the rumored site of the legendary lost Ark is at Mt. Tsurugi in Tokushima prefecture. At 1,955 meters (6,413 ft), the mountain -- known locally as "Ken-zan" -- is the highest on Shikoku and the second highest in western Japan. Mt. Tsurugi is listed as one of Japan's 100 famous mountains and is considered the most sacred peak on Shikoku. It is also regarded as one of the centers of Shugendo, an ancient ascetic religion that incorporates elements of Shintoism and Buddhism.
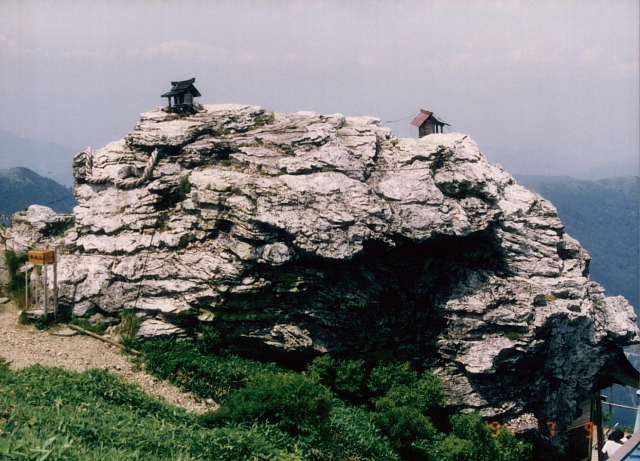

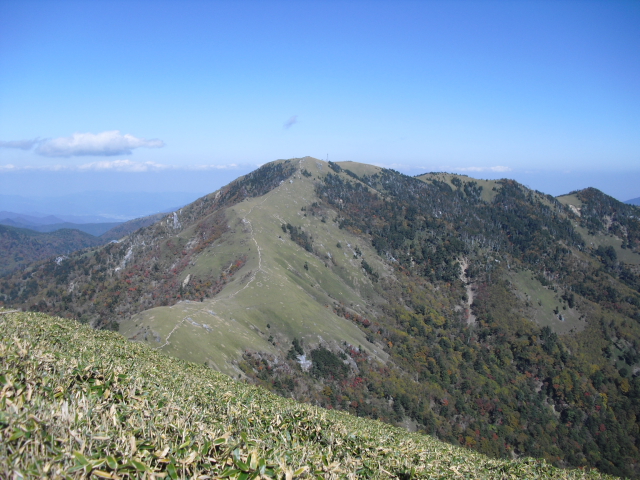
Tsurugi Jinja, a tiny shrine atop Mt. Tsurugi
Speculation surrounding the lost Ark at Mt. Tsurugi can be traced back to the work of Masanori Takane (1883-1959), a literary scholar with a deep interest in kotodama (lit. "word spirit") -- a Japanese belief that words and names hold mystical powers. Through his kotodama research, which involved the study of ancient history, philosophy, theology and cosmology, Takane came across a number of uncanny parallels between the Bible and the Kojiki ("Record of Ancient Matters"), an 8th-century collection of myths concerning the origin of the Japanese islands and Shinto kami (spirits).
In addition to suggesting possible links between the Bible and the origins of Shinto, Takane's research points to the Japanese island of Shikoku as the crucial bridge between the two. The Book of Revelation (7:1), for example, describes John's vision of "four angels standing at the four corners of the earth." Takane interpreted this as a reference to Shikoku (whose name literally means "four countries"), which is described in the Kojiki as having "four faces." After an exhaustive study of Shikoku's geography, climate, local names and folklore, Takane concluded that the lost Ark of the Covenant was buried near the peak of Mt. Tsurugi.
Here is a look inside a cave at Mt. Tsurugi, which may or may not be connected to a larger underground structure containing the lost Ark of the Covenant.
+ Video
In 1936, Takane assembled a team of archeologists and began an excavation at Mt. Tsurugi. Over the next three years, they dug up an area measuring about 150 meters (500 ft) long and found stone artifacts, paving stones, a brick arch, and evidence of tunnels. The discoveries helped lend credibility to Takane's theory that ancient people modified the peak of Mt. Tsurugi in order to hide the treasure.
Takane and others conducted excavations on Mt. Tsurugi for the next 20 years. In 1952, a former naval admiral named Eisuke Yamamoto attracted national attention when his excavation team found what appeared to be badly decomposed mummies and evidence of marble corridors. Soon after the discovery, however, both Takane and Yamamoto mysteriously stopped searching for the lost Ark at Mt. Tsurugi.
Another treasure hunter named Yoshun Miyanaka began an excavation in 1956, but the effort was short-lived. In 1964, the Japanese government established the Tsurugi-san Quasi-National Park, a 210-square-kilometer (81 sq mi) nature preserve encompassing Mt. Tsurugi and the surrounding area. Excavations on the mountain were banned for environmental reasons.
The lost Ark of the Covenant was never found at Mt. Tsurugi, but the legend lives on.
[Note: This is the latest in a series of weekly posts on mysteries and urban legends from Japan.]