Here is a look at the Kaikidan Ekotoba, a mysterious handscroll that profiles 33 legendary monsters and human oddities, mostly from the Kyushu region of Japan (with several from overseas). The cartoonish document, whose author is unknown, is believed to date from the mid-19th century. It is now in the possession of the Fukuoka City Museum.
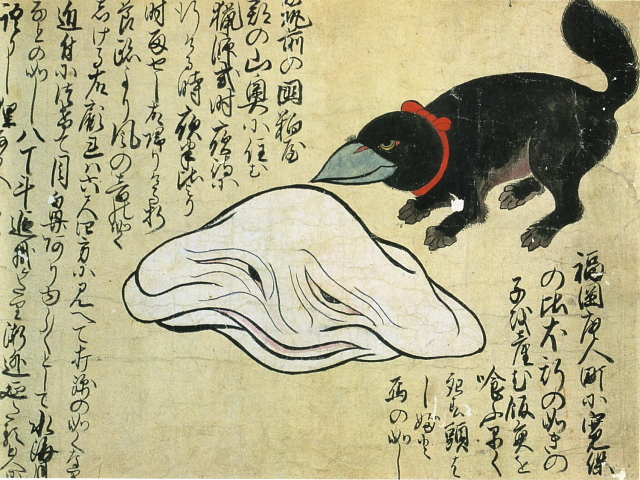

White monster/Bird-dog hybrid [+]
The black creature on the right was born by a dog that mated with a bird in the city of Fukuoka in the early 1740s. Next to the bird-dog hybrid is an amorphous white monster -- also encountered in Fukuoka -- which is said to have measured about 180 centimeters (6 ft) across. People at the time believed this creature was a raccoon dog that had shape-shifted.
* * * * *
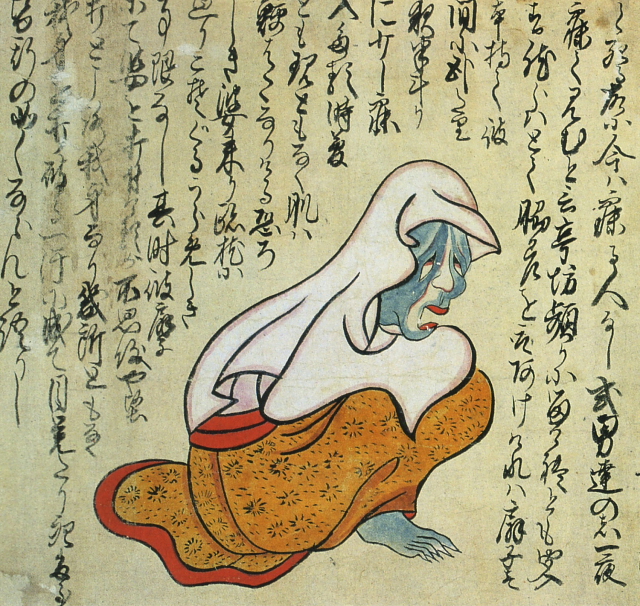

Old woman at the temple [+]
This illustration depicts a ghostly old woman known to appear late at night in a certain guest room at a temple in the Kaho area of Fukuoka prefecture. On multiple occasions, terrified lodgers ended up fatally wounding themselves after trying to strike her with a sword.
* * * * *
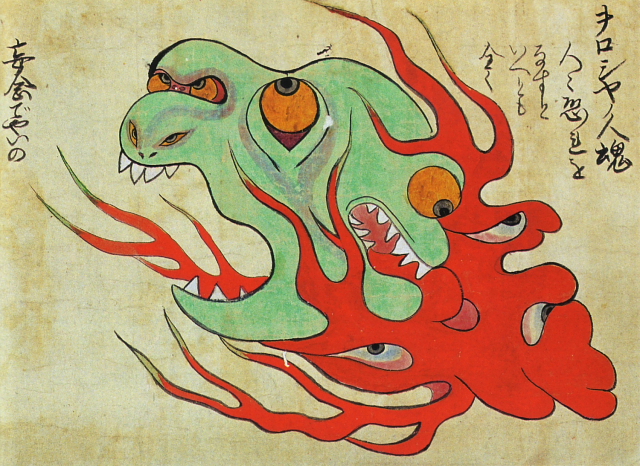

Russian fireball [+]
During heavy winds, this Russian hitodama (a fiery apparition composed of spirits of the recently departed) could be heard to say, "Oroshiya, oroshiya" ("Let me down"). There is some speculation that the author dreamed up the creature based on a play on words, as "oroshiya" sounds like the old Japanese pronunciation of "Russia."
* * * * *
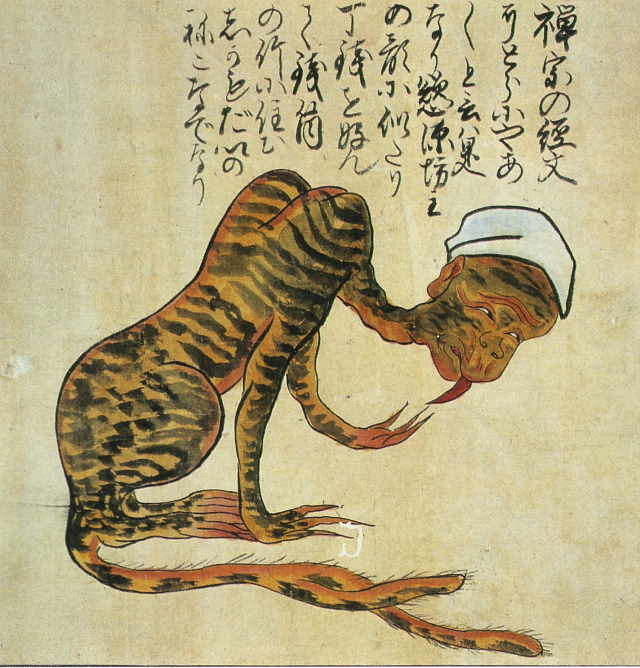
Tiger meow-meow [+]
This illustration depicts a Zenshu priest who was transformed by greed into a strange feline creature with three toes on each paw and the forked tail of a nekomata.
* * * * *
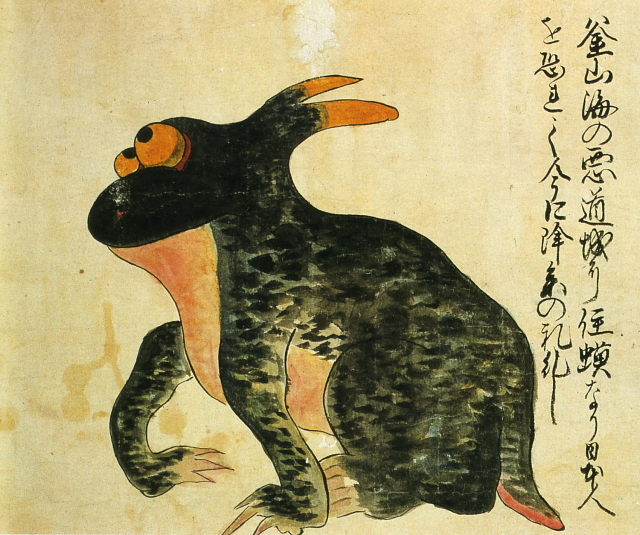

Toad from the sea near Pusan [+]
The illustration shows a fearsome horned toad said to inhabit the sea near Pusan, Korea.
* * * * *
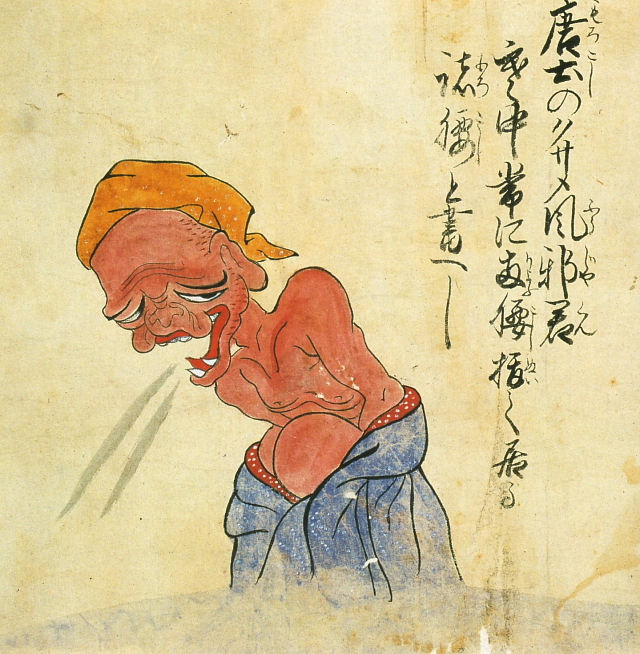
Chinese sneezer [+]
This creature resembles a half-naked, cold-ridden Chinese man and is thought to be a caricature of China, which had fallen prey to Western colonial powers.
* * * * *
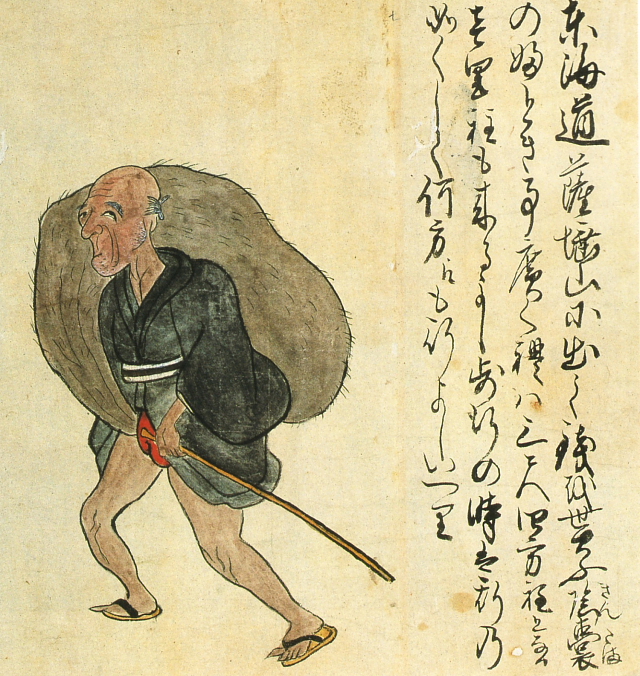
Man with oversized testicles [+]
Long ago, a man with massive testicles reportedly made a living as a sideshow attraction at Mt. Satta, on the old Tokaido Road near the city of Shizuoka. His scrotum is said to have measured about a meter across.
* * * * *

Wild woman [+]
The "wild woman" shown here appears to be an aquatic humanoid with scaly skin, webbed hands and feet (each with three fingers and toes), long black hair, and a large red mouth. People claim to have encountered the creature in the 1750s in mountain streams in the Asakura area of Fukuoka prefecture.
* * * * *
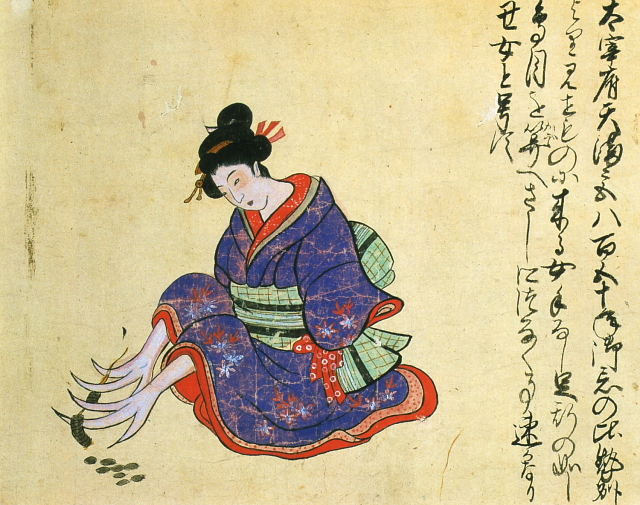

Ox woman [+]
The "ox woman" pictured here was sideshow attraction at Dazaifu Tenmangu shrine (Fukuoka prefecture) in the mid-18th century. The armless lady entertained audiences by using her peculiar feet to run string through the center holes of coins.
* * * * *
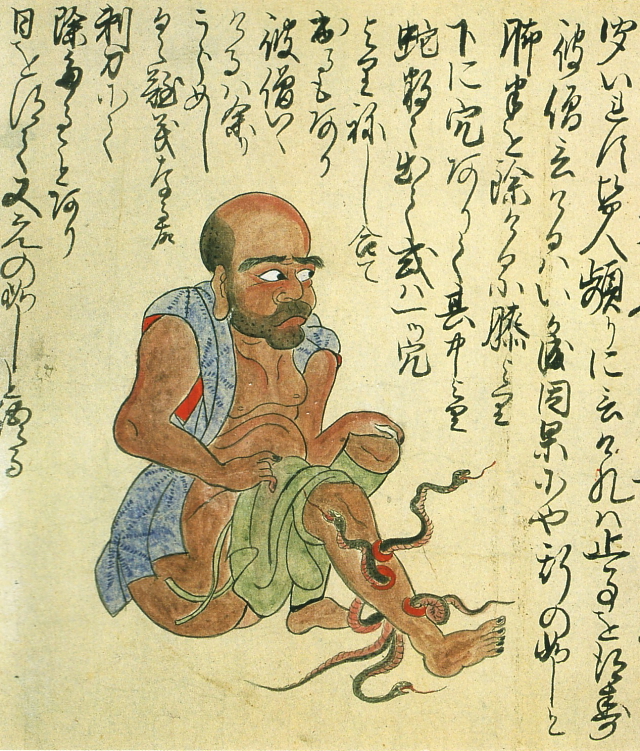

Man with snakes in his legs [+]
The illustration shows a middle-aged traveling monk from Nagano prefecture who would bathe in hot springs without removing his leggings. If anyone asked him why he did not fully undress before entering the water, he would show them the holes in his shins, which contained snakes. The man was born with snakes in his legs as punishment for misdeeds in a previous life.
* * * * *
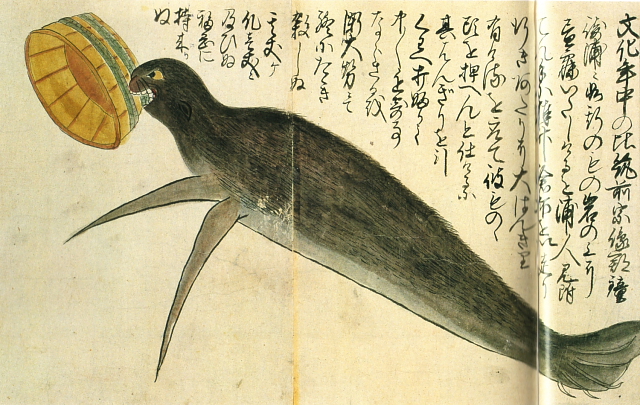

Bizarre creature at Kanezaki Inlet [+]
Many Edo-period scrolls featured illustrations of unfamiliar creatures -- animals that actually existed but were rarely seen in Japan (such as fur seals and sea lions), along with creatures generally regarded as imaginary (mermaids and kappa). This illustration shows a 3-meter-long seal that was captured in the early 19th century at Kanezaki Inlet.
* * * * *

Giant red fish [+]
This illustration depicts a giant red fish encountered by a shark fisherman in northern Japan. The head of the angry fish is said to have measured about 2 meters across.
* * * * *
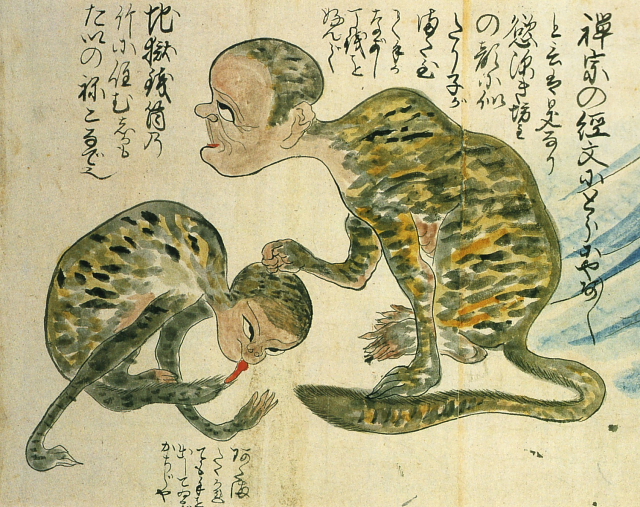
Tiger meow-meow [+]
Much like the money-hungry priest described above, the people shown here have been transformed by greed into bizarre cat creatures.
* * * * *
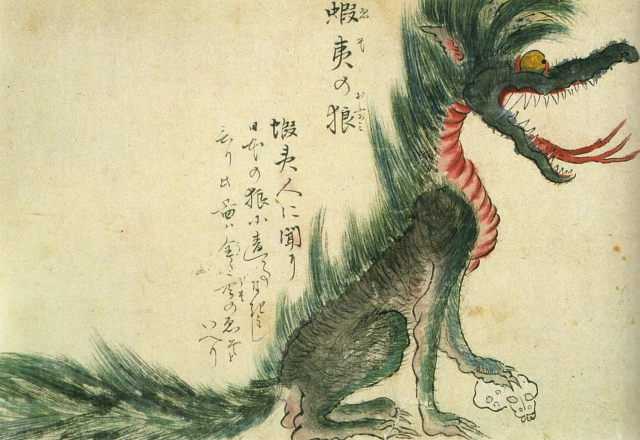

Ezo wolf [+]
This illustration shows an Ezo Wolf (a.k.a. Hokkaido Wolf), which is believed to have gone extinct in the late 19th century (after this illustration was made). The animal is seen here with its paw on a human skull.
* * * * *
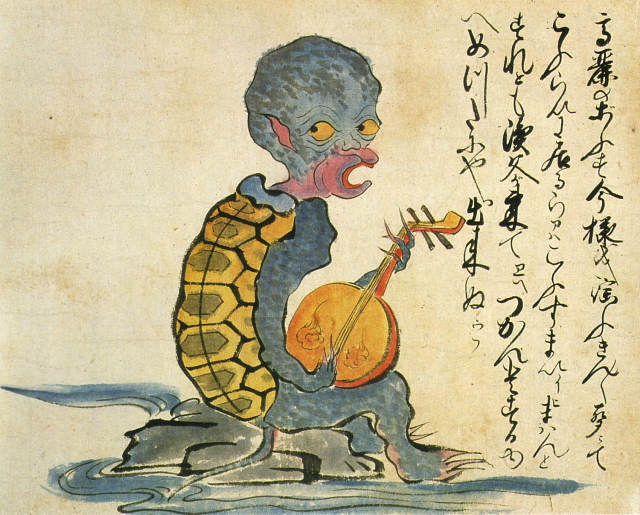
Korean monk [+]
The "Korean monk" in this illustration, seen singing and playing a gekkin (moon guitar), has the physical characteristics of a kappa (water imp).
* * * * *
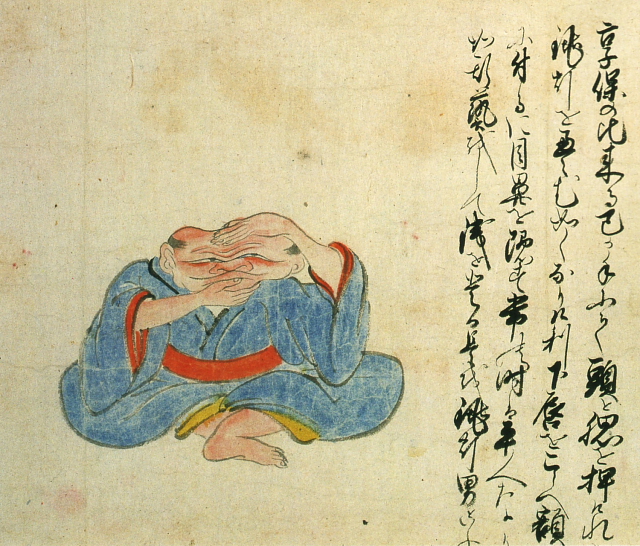
Lantern man [+]
In the early decades of the 18th century, a man with a malleable head made a living as a popular sideshow attraction. It is said that he could collapse his head like a traditional paper lantern.
* * * * *
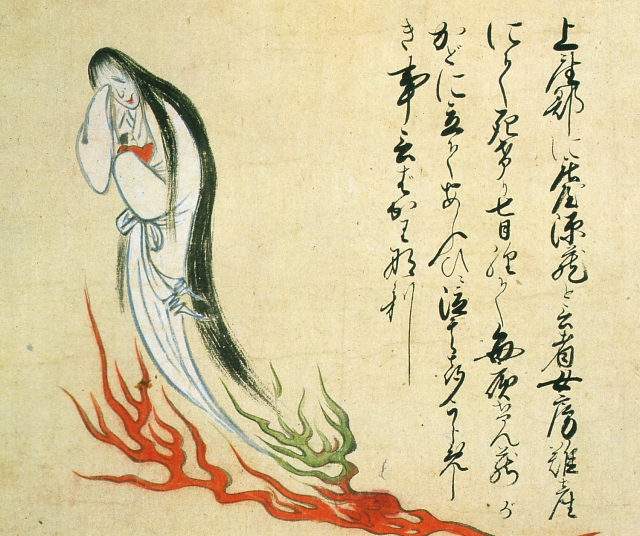

Ghost of woman with child [+]
This illustration shows the ghost of a woman from the Asakura area of Fukuoka prefecture, who died during a difficult childbirth.
* * * * *
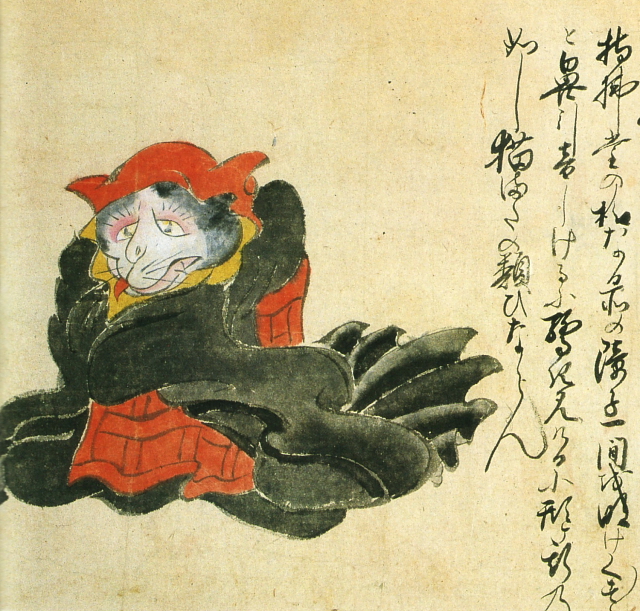

Nekomata [+]
The nekomata is a cat monster with a forked tail and a taste for human flesh. The creature's powers include the ability to talk, walk on hind legs, shape-shift, fly, and even resurrect the dead. The nekomata pictured here was encountered in the Nasuno area of Tochigi prefecture.
* * * * *
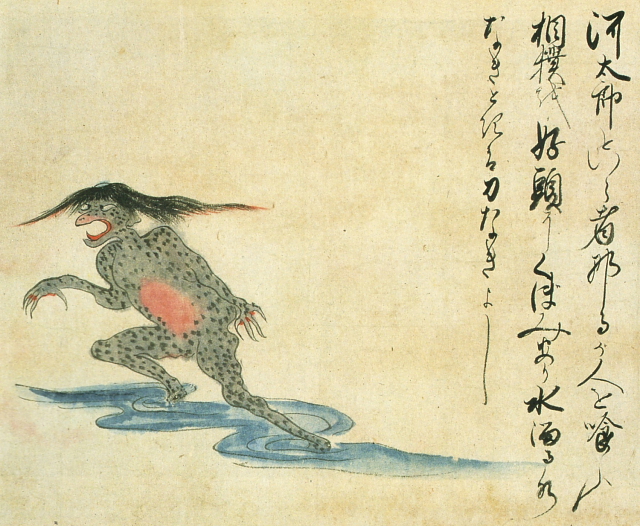

Kawataro [+]
The kawataro is a variety of kappa (water imp) which, according to the accompanying text, likes to eat people and practice sumo. An indentation on top of the creature's head is filled with water. The kawataro becomes weak when the water spills out.
* * * * *
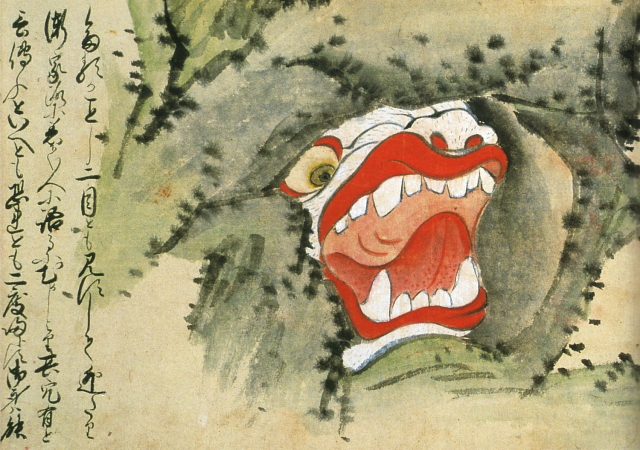

Monster hole [+]
This illustration shows a monster cave believed to exist deep in the mountains of Kumamoto prefecture. At first glance, it looks like an ordinary cave. But as you approach the entrance, the eyes and teeth become visible.
* * * * *
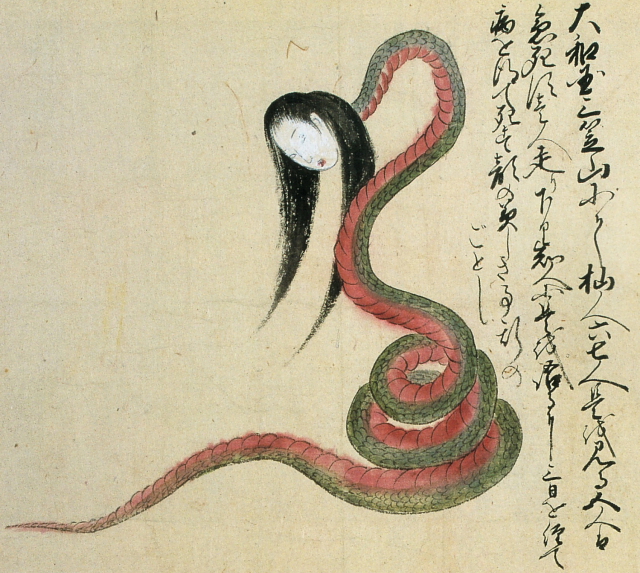
Snake woman [+]
The snake woman pictured here was reportedly encountered by six people on Mt. Mikasa in Nara prefecture. Five of the eyewitnesses died instantly. The sixth person survived long enough to make it home and tell the tale, but he grew ill and died three days later. The snake-bodied woman resembles the notorious nure-onna, except that this one has a beautiful face.
* * * * *
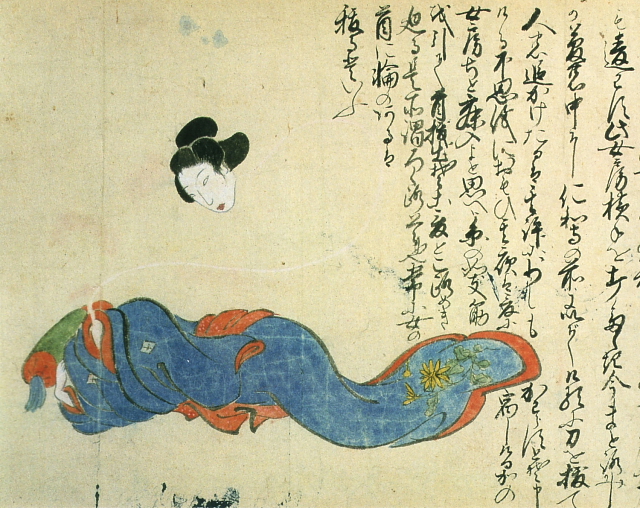

Rokurokubi [+]
This rokurokubi -- a woman with the ability to stretch her neck to extraordinary lengths -- is said to have been encountered by a messenger one night near Ninna-ji temple in Kyoto.
* * * * *
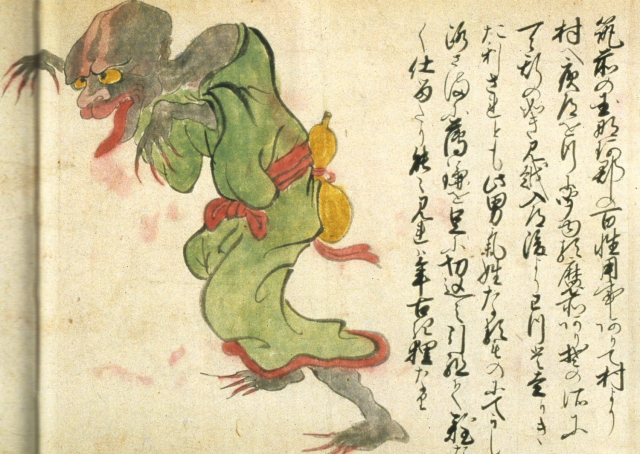

Mikoshi-nyudo [+]
The mikoshi-nyudo pictured here was encountered by a peasant on the road late one night in the Naka area of Fukuoka prefecture.
* * * * *
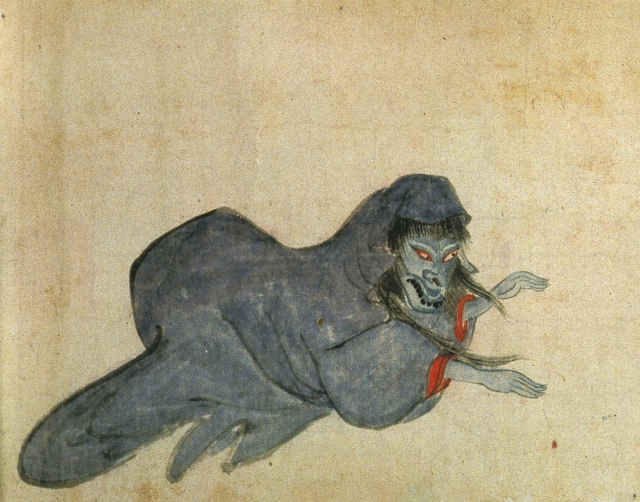

Unknown [+]
Although no explanation is given for this creature, it seems to resemble the notorious gagoze, a demon who attacked young priests at Gango-ji temple.
[Note: This is the latest in a series of weekly posts on Japanese urban legends.]









































 Left: Illustration from "Gaidan Bunbun Shuyo" shows people looking at a human-faced dog (1810)
Left: Illustration from "Gaidan Bunbun Shuyo" shows people looking at a human-faced dog (1810)






